09111 Oederan Chemnitz: 622 RESIDENTIAL UNITS. Model project for the Chemnitz technology and business park solaris, as well as the Stadtbau- und Wohnungsverwaltungsgesellschaft. 17 blocks of flats were renovated, 7 of them were equipped with 100 sqm collector surface each. Year of construction: 2000
Thema: Energy and climate protection
 10963 Berlin-Kreuzberg: "International Building Exhibition", 106 units, completed in 1987 / optimisation and redesign in 2006, grey water recycling plant for 250 tenants, saving 3 million litres of fresh water per year.
10963 Berlin-Kreuzberg: "International Building Exhibition", 106 units, completed in 1987 / optimisation and redesign in 2006, grey water recycling plant for 250 tenants, saving 3 million litres of fresh water per year.
 10965 Berlin: Cooperative for self-managed, social and ecological living eG. In the Möckernkiez model project, 471 residential units were created in 14 residential buildings. They were built according to the passive house standard and ecological building criteria. 0.21 parking spaces per unit. Property size: 30,000 m². It is barrier-free throughout and designed to be free of car traffic at the neighbourhood level. The Möckernkiez is located directly adjacent to the southeastern entrances of the Park am Gleisdreieck. Completion: 2018
10965 Berlin: Cooperative for self-managed, social and ecological living eG. In the Möckernkiez model project, 471 residential units were created in 14 residential buildings. They were built according to the passive house standard and ecological building criteria. 0.21 parking spaces per unit. Property size: 30,000 m². It is barrier-free throughout and designed to be free of car traffic at the neighbourhood level. The Möckernkiez is located directly adjacent to the southeastern entrances of the Park am Gleisdreieck. Completion: 2018
 12487 Berlin-Johannisthal: 20 houses with 22 residential units (KfW 40-60) for 70 small and large people, ecological housing project. Number of parking spaces: 0.3 PkWs/WE, 100 m² solar collectors (50 kW), 23 kW photovoltaic system, 99 kW wood pellet system (with exhaust gas heat exchanger, downstream flue gas scrubber and condensate heat exchanger), 600 m³ grey water system, completion: 2007
12487 Berlin-Johannisthal: 20 houses with 22 residential units (KfW 40-60) for 70 small and large people, ecological housing project. Number of parking spaces: 0.3 PkWs/WE, 100 m² solar collectors (50 kW), 23 kW photovoltaic system, 99 kW wood pellet system (with exhaust gas heat exchanger, downstream flue gas scrubber and condensate heat exchanger), 600 m³ grey water system, completion: 2007
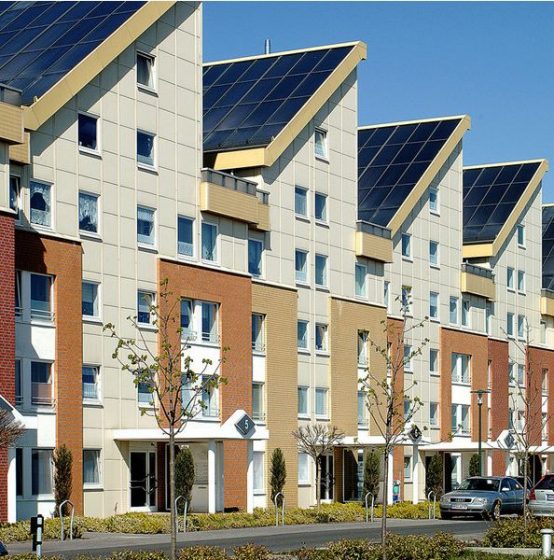
 13156 Berlin-Pankow: Consortium Winfried Brenne Architekten / Joachim Eble Architektur, 226 units, largest roof-integrated solar power system on residential buildings in Europe; research study on the costs of ecological building materials (comparison with Berlin reference house). Reference: 1999
13156 Berlin-Pankow: Consortium Winfried Brenne Architekten / Joachim Eble Architektur, 226 units, largest roof-integrated solar power system on residential buildings in Europe; research study on the costs of ecological building materials (comparison with Berlin reference house). Reference: 1999
 21035 Hamburg-Allermöhe: 36 completed units in semi-detached and terraced houses, one of the older ecological housing estates in Germany; largely built from 1985-96, the last house was built in 2003. Compost toilets, reed sewage treatment plant, biological building materials. "Interessengemeinschaft Ökologisches Bauen Allermöhe", planning/construction management: J. Lupp architect; Vollbracht und Bäumer architects; T. Keidel, M. Uhlenhaut, Hamburg; Cordes, Rotenburg/ Wümme. Awards Timber Construction Prize Northern Germany 1988.
21035 Hamburg-Allermöhe: 36 completed units in semi-detached and terraced houses, one of the older ecological housing estates in Germany; largely built from 1985-96, the last house was built in 2003. Compost toilets, reed sewage treatment plant, biological building materials. "Interessengemeinschaft Ökologisches Bauen Allermöhe", planning/construction management: J. Lupp architect; Vollbracht und Bäumer architects; T. Keidel, M. Uhlenhaut, Hamburg; Cordes, Rotenburg/ Wümme. Awards Timber Construction Prize Northern Germany 1988.
 22045 Hamburg-JenfeldHAMBURG WATER Cycle®, an urban quarter with 835 residential units, 630 of them in new buildings, and commercial space for around 2000 residents is being built on 35 ha of the former Lettow-Vorbeck barracks. Project costs: approx. 250 million euros. The most far-reaching project of a decentralised water supply and disposal system currently in Europe: vacuum toilets, biogas production and waste water separation (HAMBURG WATER Cycle®). The biogas produced will be used to generate heat and electricity for the new district in a climate-neutral manner in the district's own combined heat and power plant. The project will thus enable climate-neutral living and sustainable drainage.
22045 Hamburg-JenfeldHAMBURG WATER Cycle®, an urban quarter with 835 residential units, 630 of them in new buildings, and commercial space for around 2000 residents is being built on 35 ha of the former Lettow-Vorbeck barracks. Project costs: approx. 250 million euros. The most far-reaching project of a decentralised water supply and disposal system currently in Europe: vacuum toilets, biogas production and waste water separation (HAMBURG WATER Cycle®). The biogas produced will be used to generate heat and electricity for the new district in a climate-neutral manner in the district's own combined heat and power plant. The project will thus enable climate-neutral living and sustainable drainage.
22844 Norderstedt: 36 terraced houses in low-energy construction, all roofs are completely greened, combined heat and power plant. Completion: ~2002
22926 AhrensburgSite area: 6.4 ha; 15 houses with 1 - 14 flats with high ecological standards (110 units); 40% of the built-up area for commercial use. Largest residential project with living and working in Schleswig-Holstein. Completion: 2012
 23569 Lübeck-Kücknitz: 36 social housing units in 3 buildings in low-energy and timber construction with a total living space of 2,213 m². Pilot project as part of the "Resource-saving construction" programme funded by the state of Schleswig-Holstein. The main premise in the implementation of this pilot project was the synthesis of healthy living, energy and cost-saving construction with child and family-friendly floor plans. Completion: 1998
23569 Lübeck-Kücknitz: 36 social housing units in 3 buildings in low-energy and timber construction with a total living space of 2,213 m². Pilot project as part of the "Resource-saving construction" programme funded by the state of Schleswig-Holstein. The main premise in the implementation of this pilot project was the synthesis of healthy living, energy and cost-saving construction with child and family-friendly floor plans. Completion: 1998
 23617 Stockelsdorf: 24 flats in 13 terraced houses, two semi-detached houses, 1 detached house (and ... ?). Timber frame construction with solid infill (bricks) in the south façade and highly insulated infill (cellulose) in the north façades. Conservatories, combined heat and power unit, rainwater utilisation, PVC-free construction, healthy living materials and paintwork. Architectural partnership Rolf Zeschke (Bad Schwartau) & Uwe Witaszek. Completion: ~1997
23617 Stockelsdorf: 24 flats in 13 terraced houses, two semi-detached houses, 1 detached house (and ... ?). Timber frame construction with solid infill (bricks) in the south façade and highly insulated infill (cellulose) in the north façades. Conservatories, combined heat and power unit, rainwater utilisation, PVC-free construction, healthy living materials and paintwork. Architectural partnership Rolf Zeschke (Bad Schwartau) & Uwe Witaszek. Completion: ~1997
24159 Kiel-Pries: In 7 buildings around a car-free courtyard of approx. 6,500 m², a total of 27 apartments between approx. 40 and approx. 125 m² living space and a community house with a grass roof, as well as an organic food store in an existing building have been created in a space-saving architecture. Four of the buildings are new constructions, in the other two buildings old building substance was redeveloped. Completion: 2003
28357 Bremen-Hollerland: 200 units (not realised); model photos, well-analysed study on the failure of the project. The most important reasons: "too sterile architecture; too expensive although low-cost construction was promised; too far outside the city; the fact that the city railway was not routed to the new district after all; generally poor construction activity; major employer in Bremen went bankrupt." However, the Hollerland project caused a lot of media hype and is regarded as a model for many other projects that have since been realised, such as "Bremen-Grünenstrasse", although not on the outskirts of the city but in the city centre.
30539 Hanover-Kronsberg: Sub-project of the Expo 2000 new housing development. 106 apartments with large solar collectors on the roofs, as well as solar local heating with seasonal storage. It is located in the southeastern part of the district. Completion: 2000
30629 Hanover-Miesburg: "Regenbogensiedlung", 111 council flats, GFZ 0.88. 9,000 m² living space. Occupancy 1996. 900 euros/m². Architect: Schmitz, Aachen, property developer Gundlach, Philipp Holzmann AG - CHP, low-energy construction, extensive green roof - pergola development
 33649 Bielefeld-Quelle: 96 units, architect: Hans-Friedrich Bültmann, special features: all buildings are equipped with composting toilets and the highest composting toilet in Europe is located on the 5th floor. Further water measures: rainwater infiltration, own drinking water source; a reed sewage treatment plant was planned but could not be realised. Energy: BHKW, local heating network, internal cable TV, telephone distribution. Social: KiTa, craftsmen's yard, cooperative project. Economy: Development as a large plot, low-cost construction with partly much own work. Construction time: 1997
33649 Bielefeld-Quelle: 96 units, architect: Hans-Friedrich Bültmann, special features: all buildings are equipped with composting toilets and the highest composting toilet in Europe is located on the 5th floor. Further water measures: rainwater infiltration, own drinking water source; a reed sewage treatment plant was planned but could not be realised. Energy: BHKW, local heating network, internal cable TV, telephone distribution. Social: KiTa, craftsmen's yard, cooperative project. Economy: Development as a large plot, low-cost construction with partly much own work. Construction time: 1997
 44649 Herne: This is not a housing estate, but the concept could equally be applied to housing. The Naturhuset apartment house by Bengt Warne in Stockholm was one of the first pioneering buildings to implement the house-in-house principle with a shell of glass. Also the Student dormitory ESA in Kaiserslautern is built like this. The project in Herne, however, is the most spectacular of its kind in this form.
Planned in partnership by the German architectural firm HHS Planer & Architekten AG and the French architectural firm Jourda & Perraudin (Francoise Helene Jourda and Gilles Perraudin), the building is enclosed in a glass climate shell that creates a Mediterranean climate similar to that in Nice. This is on average 5 °C warmer than the outside temperature. Water features, earth channels and large gates prevent overheating in summer. The solar system in the roof, was the largest building-integrated system of its kind at the time. The supports inside are made of 56 spruce trunks. Completion: 1999
44649 Herne: This is not a housing estate, but the concept could equally be applied to housing. The Naturhuset apartment house by Bengt Warne in Stockholm was one of the first pioneering buildings to implement the house-in-house principle with a shell of glass. Also the Student dormitory ESA in Kaiserslautern is built like this. The project in Herne, however, is the most spectacular of its kind in this form.
Planned in partnership by the German architectural firm HHS Planer & Architekten AG and the French architectural firm Jourda & Perraudin (Francoise Helene Jourda and Gilles Perraudin), the building is enclosed in a glass climate shell that creates a Mediterranean climate similar to that in Nice. This is on average 5 °C warmer than the outside temperature. Water features, earth channels and large gates prevent overheating in summer. The solar system in the roof, was the largest building-integrated system of its kind at the time. The supports inside are made of 56 spruce trunks. Completion: 1999







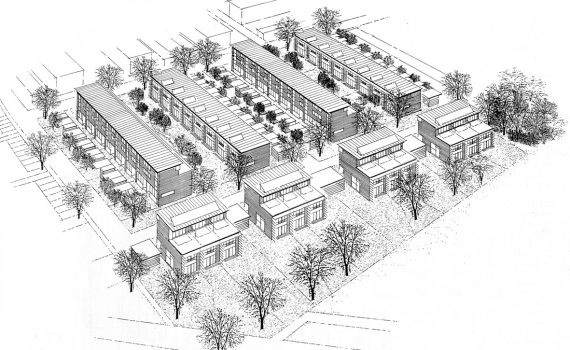































 37083 Göttingen: Building group "Auf den Terrassen". Planning: Baufrösche (Kassel)
37083 Göttingen: Building group "Auf den Terrassen". Planning: Baufrösche (Kassel)






