The state of Baden-Württemberg is setting an example in climate protection: by 2040 at the latest, the state administration is to operate in a climate-neutral manner. The new Climate Protection Foundation supports it in this by using the interest on its share capital to promote research and development as well as educational projects in the field of climate protection. In addition, the state, municipalities, companies and all citizens can offset their CO2 emissions through compensation payments and thus become climate neutral. The cooperation partner will be the non-profit climate protection organisation myclimate Germany.
Kategorie für Blog: Climate protection
 "New large-scale construction projects and ecological innovations have ensured that Malmö is now a prime example of the direct transition from an industrial metropolis to a sustainable eco city. The secret recipe: the city not only relied on innovative technologies, but above all on the active participation of citizens in the transformation."
"New large-scale construction projects and ecological innovations have ensured that Malmö is now a prime example of the direct transition from an industrial metropolis to a sustainable eco city. The secret recipe: the city not only relied on innovative technologies, but above all on the active participation of citizens in the transformation."
On 22.12.2020, the Senate passed the first legal ordinance on the Hamburg Climate Protection Act. This regulates the concrete implementation of the solar roof obligation and the integration of renewable energies when replacing heating systems. With these regulations, Hamburg is one of the pioneers in climate protection in the building sector nationwide.
A new study from Denmark takes a look at the costs of sustainable building construction and shows that more sustainable does not automatically mean more expensive. On the contrary. The study by Buus Consult on behalf of the DGNB system partner from Denmark, the Green Building Council Denmark, now provides clarity. In the study, it takes a close look at 37 DGNB-certified buildings.
Constance receives project funding for "Hafner KliEn" from the 7th Energy Research Programme of the Federal Government The city of Constance is striving for sustainable urban development. This should include consideration of the triad of sufficiency, efficiency and substitution in the area of energy policy decisions and climate protection. This also and especially applies to the new city district [...].
 In the context of the Green Deal, the EU's tightened targets on the path to climate neutrality envisage a reduction in CO2 emissions of 55% by 2030 and 100% by 2050. Against the background of these tightened parameters, the question arises as to the impact on the energy transition in Germany. Based on its energy system model REMod, Fraunhofer ISE has calculated the consequences of the new EU targets for the expansion of renewable energies in Germany and now presents the results in a short study.
In the context of the Green Deal, the EU's tightened targets on the path to climate neutrality envisage a reduction in CO2 emissions of 55% by 2030 and 100% by 2050. Against the background of these tightened parameters, the question arises as to the impact on the energy transition in Germany. Based on its energy system model REMod, Fraunhofer ISE has calculated the consequences of the new EU targets for the expansion of renewable energies in Germany and now presents the results in a short study.
Emissions targets, some of them significantly improved, show effectiveness of Paris Agreement / But too few commitments for financing climate protection and adaptation to climate change in poorer countries / Chancellor Merkel must swiftly launch international process for additional climate financing
 With the portal https://energiewendedörfer.de the University of Kassel and Georg-August-Universität Göttingen will present the initial results from the joint project "Innovative concepts and business models for sustainable bioenergy villages - climate-friendly, democratic, citizen-centred". In particular, concepts are being developed for bioenergy and biogas plants that can enable continued economic operation after the current 20-year EEG phase.
With the portal https://energiewendedörfer.de the University of Kassel and Georg-August-Universität Göttingen will present the initial results from the joint project "Innovative concepts and business models for sustainable bioenergy villages - climate-friendly, democratic, citizen-centred". In particular, concepts are being developed for bioenergy and biogas plants that can enable continued economic operation after the current 20-year EEG phase.

 The German Solar Energy Society e.V. (DGS) and the energy advice service of the consumer advice centre have been cooperating with each other since 1 December 2020. Consumer enquiries from both institutions are answered by the energy advisors of the consumer advice centre. In return, the DGS trains the advisors of the consumer advice centre in the subject area of plug-in solar devices.
The German Solar Energy Society e.V. (DGS) and the energy advice service of the consumer advice centre have been cooperating with each other since 1 December 2020. Consumer enquiries from both institutions are answered by the energy advisors of the consumer advice centre. In return, the DGS trains the advisors of the consumer advice centre in the subject area of plug-in solar devices.
 The ecological model settlement on a former barracks site in Munich sets new standards in timber construction. Various timber construction methods and building types up to seven storeys are being tested side by side in eight building projects with the aim of a final scientific evaluation. Timber frame, timber frame and timber hybrid construction methods are being used.
The ecological model settlement on a former barracks site in Munich sets new standards in timber construction. Various timber construction methods and building types up to seven storeys are being tested side by side in eight building projects with the aim of a final scientific evaluation. Timber frame, timber frame and timber hybrid construction methods are being used.
 The state of Lower Saxony has launched a new funding programme for battery storage systems. The funding guideline was published in the Lower Saxony Ministerial Gazette on 21 October. Applications can be submitted to the NBank with immediate effect.
The subsidy of up to 40 per cent of the net investment costs of a battery storage system applies in connection with the new construction or expansion of PV systems (at least 4 kWp). In addition to natural persons, grant recipients can also be companies, legal entities, local authorities and many others.
The state of Lower Saxony has launched a new funding programme for battery storage systems. The funding guideline was published in the Lower Saxony Ministerial Gazette on 21 October. Applications can be submitted to the NBank with immediate effect.
The subsidy of up to 40 per cent of the net investment costs of a battery storage system applies in connection with the new construction or expansion of PV systems (at least 4 kWp). In addition to natural persons, grant recipients can also be companies, legal entities, local authorities and many others.
 "To be climate neutral by 2050, we not only need to make additional investments in green and innovative technologies of the future. Above all, we also need a shift from existing investments in 'brown' raw materials such as coal, oil and gas to 'green' climate-friendly technologies. The phase-out of fossil fuels must be global and rapid, in line with the goals of the World Climate Conference. Only in this way can we realistically achieve the climate protection goals. Churches, municipalities and also companies are setting new standards here and demonstrating the feasibility of the changeover in both ecological and economic terms," said Environment Minister Ulrike Höfken today at the event "Divestment and Sustainable Finance", which took place during the Climate Protection Weeks in Rhineland-Palatinate.
"To be climate neutral by 2050, we not only need to make additional investments in green and innovative technologies of the future. Above all, we also need a shift from existing investments in 'brown' raw materials such as coal, oil and gas to 'green' climate-friendly technologies. The phase-out of fossil fuels must be global and rapid, in line with the goals of the World Climate Conference. Only in this way can we realistically achieve the climate protection goals. Churches, municipalities and also companies are setting new standards here and demonstrating the feasibility of the changeover in both ecological and economic terms," said Environment Minister Ulrike Höfken today at the event "Divestment and Sustainable Finance", which took place during the Climate Protection Weeks in Rhineland-Palatinate.
 Since April 2020, the Öko-Institut has been conducting research into how urban neighbourhoods can be sustainably transformed, using two neighbourhoods in the swarming city of Darmstadt as examples, in the project Transformative Strategies for Integrated Neighbourhood Development (TRASIQ 2). The Federal Ministry of Education and Research is funding the project, which is led by the Öko-Institut and involves the City of Darmstadt, the Institute for Regional and Urban Development Research (ILS) and the "Team Ewen" agency.
Since April 2020, the Öko-Institut has been conducting research into how urban neighbourhoods can be sustainably transformed, using two neighbourhoods in the swarming city of Darmstadt as examples, in the project Transformative Strategies for Integrated Neighbourhood Development (TRASIQ 2). The Federal Ministry of Education and Research is funding the project, which is led by the Öko-Institut and involves the City of Darmstadt, the Institute for Regional and Urban Development Research (ILS) and the "Team Ewen" agency.
Mobility, heat and living space
The project focuses on the research topics of mobility, heat supply and efficient use of living space. Heat supply is an important key to climate-friendly living. How and where, for example, can district heating be expanded in existing properties? How can we increase the share of renewable energies in the heat supply? The size of the living space also contributes to how environmentally friendly a person lives. What needs to be done to ensure that people have the living space they need in their particular phase of life through intelligent apartment swaps? How can neighbourhoods be redesigned so that residents can organise their mobility ecologically? With the gradual dismantling of ten particularly climate-damaging subsidies in the energy, transport and agricultural sectors, Germany could generate up to 46 billion euros in revenue annually. This is the result of a new study by the "Forum Ökologisch-Soziale Marktwirtschaft" commissioned by Greenpeace.
With the gradual dismantling of ten particularly climate-damaging subsidies in the energy, transport and agricultural sectors, Germany could generate up to 46 billion euros in revenue annually. This is the result of a new study by the "Forum Ökologisch-Soziale Marktwirtschaft" commissioned by Greenpeace.
 Dr. Kirsten David, a researcher at HafenCity University (HCU) Hamburg, has developed an innovative method for determining rent increases after energy efficiency measures: By means of functional cost splitting, rent increases become appropriate and comprehensible. The planning of the energetic measures is also ecologically optimized. For her dissertation entitled "Functional Cost Splitting for the Determination of Rent Increases after Energy Efficiency Measures", the scientist today receives the "BUND Research Award 2020". With the research award, the Bund für Umwelt- und Naturschutz (BUND) honors scientific work on sustainable development.
Dr. Kirsten David, a researcher at HafenCity University (HCU) Hamburg, has developed an innovative method for determining rent increases after energy efficiency measures: By means of functional cost splitting, rent increases become appropriate and comprehensible. The planning of the energetic measures is also ecologically optimized. For her dissertation entitled "Functional Cost Splitting for the Determination of Rent Increases after Energy Efficiency Measures", the scientist today receives the "BUND Research Award 2020". With the research award, the Bund für Umwelt- und Naturschutz (BUND) honors scientific work on sustainable development.
Grant of 900 euros per charging point For charging stations at privately used parking spaces of residential buildings For owners and condominium owners' associations, for tenants and landlords The electricity must come 100 percent from renewable energies Applications for funding can be submitted to the Kreditanstalt für Wiederaufbau (KfW) from 24 November 2020. Information: […]
 Wohnungsbaugenossenschaft Neues Berlin and Berliner Stadtwerke have agreed on another joint tenant power project. Six solar power systems with an output of around 500 kilowatts are being built in the Mühlengrund housing estate in Hohenschönhausen. Tenants of more than 1,100 apartments will soon be able to benefit from green electricity from their own roofs.
Wohnungsbaugenossenschaft Neues Berlin and Berliner Stadtwerke have agreed on another joint tenant power project. Six solar power systems with an output of around 500 kilowatts are being built in the Mühlengrund housing estate in Hohenschönhausen. Tenants of more than 1,100 apartments will soon be able to benefit from green electricity from their own roofs.
 From 1 January 2021, climate-damaging fossil fuels will be subject to a price of 25 euros per tonne of CO2 is proven. This means that oil and diesel will become more expensive by 7.9 cents per litre, petrol by 7 cents per litre and natural gas by 0.6 cents per kilowatt hour. Citizens will be relieved of the additional costs, among other things, by a reduction in the price of electricity. The amendment, which had already been passed by the Bundestag on Thursday, also passed the Bundesrat today. The Fuel Emission Trading Act (BEHG) is designed to reduce CO2-price in the form of national certificate trading for the heating and transport sectors.
From 1 January 2021, climate-damaging fossil fuels will be subject to a price of 25 euros per tonne of CO2 is proven. This means that oil and diesel will become more expensive by 7.9 cents per litre, petrol by 7 cents per litre and natural gas by 0.6 cents per kilowatt hour. Citizens will be relieved of the additional costs, among other things, by a reduction in the price of electricity. The amendment, which had already been passed by the Bundestag on Thursday, also passed the Bundesrat today. The Fuel Emission Trading Act (BEHG) is designed to reduce CO2-price in the form of national certificate trading for the heating and transport sectors.
 Glaciers are melting, sea levels are rising, heat waves and heavy rainfall are increasing: The consequences of climate change are visible and tangible worldwide, and the window of opportunity to act is shrinking. In order to significantly limit the global effects of climate change, the emission of greenhouse gases on earth must be drastically reduced. The agreement reached by the international community in Paris in 2015 sets the goal of limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, but preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius. Now, the Wuppertal Institute presented a study with possible cornerstones that can help to achieve the 1.5 degree target by 2035. The study shows that a climate-neutral energy system by 2035 is very ambitious, but in principle feasible, provided that all possible strategies from today's perspective are bundled. This requires, above all, bringing forward and intensifying measures that are described in many studies as necessary to achieve greenhouse gas neutrality by 2050.
Glaciers are melting, sea levels are rising, heat waves and heavy rainfall are increasing: The consequences of climate change are visible and tangible worldwide, and the window of opportunity to act is shrinking. In order to significantly limit the global effects of climate change, the emission of greenhouse gases on earth must be drastically reduced. The agreement reached by the international community in Paris in 2015 sets the goal of limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, but preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius. Now, the Wuppertal Institute presented a study with possible cornerstones that can help to achieve the 1.5 degree target by 2035. The study shows that a climate-neutral energy system by 2035 is very ambitious, but in principle feasible, provided that all possible strategies from today's perspective are bundled. This requires, above all, bringing forward and intensifying measures that are described in many studies as necessary to achieve greenhouse gas neutrality by 2050.
 Solarserver reports on the world's largest solar heating plant, which has been in operation in China since 2016. It consists of parabolic trough collectors.
On the roof of a XuChen factory building next to the company headquarters are 22,000 m2 collector area, a further 71,000 m2 collector area are implemented as ground-mounted systems. Together they deliver an output of 65 MWth. With concentrating collectors, it would thus be the largest solar heating plant of its kind. An even larger one is the Danish Silkeborg plant (110 MWth)which, however, is equipped with a different collector technology.
For comparison: the largest German solar thermal system that supplies a settlement, neighbourhood or district currently has just 14,800 m²
Solarserver reports on the world's largest solar heating plant, which has been in operation in China since 2016. It consists of parabolic trough collectors.
On the roof of a XuChen factory building next to the company headquarters are 22,000 m2 collector area, a further 71,000 m2 collector area are implemented as ground-mounted systems. Together they deliver an output of 65 MWth. With concentrating collectors, it would thus be the largest solar heating plant of its kind. An even larger one is the Danish Silkeborg plant (110 MWth)which, however, is equipped with a different collector technology.
For comparison: the largest German solar thermal system that supplies a settlement, neighbourhood or district currently has just 14,800 m²
 Hydrogen is an important alternative for sectors stuck in the fossil fuel economy. As national governments and European parliamentarians negotiate the EU's hydrogen strategy, EASAC issues a new commentary. "Hydrogen can help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels," says William Gillett, Director of EASAC's Energy Programme. "But the climate benefits are limited if we use fossil fuels to produce it - even with carbon capture and storage. The EU must put an end to fossil fuel subsidies. The rapidly growing demand for hydrogen must be met by a massive increase in electricity generation from renewables, together with certified imports from third countries."
Hydrogen is an important alternative for sectors stuck in the fossil fuel economy. As national governments and European parliamentarians negotiate the EU's hydrogen strategy, EASAC issues a new commentary. "Hydrogen can help reduce our dependence on fossil fuels," says William Gillett, Director of EASAC's Energy Programme. "But the climate benefits are limited if we use fossil fuels to produce it - even with carbon capture and storage. The EU must put an end to fossil fuel subsidies. The rapidly growing demand for hydrogen must be met by a massive increase in electricity generation from renewables, together with certified imports from third countries."
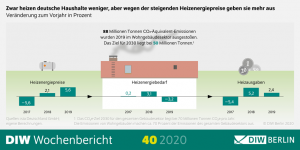 Annual DIW Heat Monitor based on data from energy service provider ista Deutschland GmbH: Heating energy demand in residential buildings declines again for the first time since 2015 - Rising prices, however, cause heating expenditure to increase by 2.4 percent - CO2emissions have fallen by 21 percent overall since 2010, but by only 2.6 percent when adjusted for temperature - Energy-efficient renovation in residential buildings almost stagnant
Annual DIW Heat Monitor based on data from energy service provider ista Deutschland GmbH: Heating energy demand in residential buildings declines again for the first time since 2015 - Rising prices, however, cause heating expenditure to increase by 2.4 percent - CO2emissions have fallen by 21 percent overall since 2010, but by only 2.6 percent when adjusted for temperature - Energy-efficient renovation in residential buildings almost stagnant
 "Solar energy is a fundamental pillar of the energy transition. In order to further support this and to achieve our goal - a complete power supply from renewable energies by 2030 - we are further expanding our successful solar offensive: In addition to expanding the solar storage programme, which is in high demand, we are currently developing a solar register for Rhineland-Palatinate. In addition, we will also promote solar carports, balcony plug-in modules, wall boxes or agro-PV projects in the future," announced Environment and Energy Minister Ulrike Höfken during the event under the motto "Solar Offensive Rhineland-Palatinate: Investments for Climate and Economy" as part of the series "Wednesdays in the MUEEF" in Mainz today.
"Solar energy is a fundamental pillar of the energy transition. In order to further support this and to achieve our goal - a complete power supply from renewable energies by 2030 - we are further expanding our successful solar offensive: In addition to expanding the solar storage programme, which is in high demand, we are currently developing a solar register for Rhineland-Palatinate. In addition, we will also promote solar carports, balcony plug-in modules, wall boxes or agro-PV projects in the future," announced Environment and Energy Minister Ulrike Höfken during the event under the motto "Solar Offensive Rhineland-Palatinate: Investments for Climate and Economy" as part of the series "Wednesdays in the MUEEF" in Mainz today.
"The world's water resources are currently facing the greatest threat in the history of mankind," write aquatic ecologists in their recently published statement paper. More than one hundred professional societies of aquatic ecosystem research around the globe have signed the joint statement. In it, the researchers show the dramatic effects that climate change is having on aquatic ecosystems worldwide. They call for immediate concerted action by politics, business, science and society to halt the progress of climate change.
 As stated by EU Commission President Ursula von der Leyen in her State of the Union address announced, the European Commission today (Thursday) proposed that EU greenhouse gas emissions should fall by at least 55 percent by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. The previous target was 40 percent. The new target is based on a comprehensive impact assessment of the social, economic and environmental consequences. This shows that 55 percent less emissions is realistic and feasible. The new climate target will help support Europe's economic recovery from the coronavirus pandemic. It also demonstrates the EU's global leadership in the run-up to the next UN climate conference (COP26).
As stated by EU Commission President Ursula von der Leyen in her State of the Union address announced, the European Commission today (Thursday) proposed that EU greenhouse gas emissions should fall by at least 55 percent by 2030 compared to 1990 levels. The previous target was 40 percent. The new target is based on a comprehensive impact assessment of the social, economic and environmental consequences. This shows that 55 percent less emissions is realistic and feasible. The new climate target will help support Europe's economic recovery from the coronavirus pandemic. It also demonstrates the EU's global leadership in the run-up to the next UN climate conference (COP26).
CO2-Emissions should be reduced by 65 percent over the next ten years compared to 1990 in order to achieve climate neutrality - Energy system must be converted to 100 percent renewable energies by 2040 - Investment of 3,000 billion euros required to meet European Green Deal and Paris climate targets - German EU Council Presidency can ensure that Corona aid packages link economic stimulus with climate protection
Climate protection is important to over 80 percent of Germans - but this should not be reflected in higher rental costs. In order to increase the acceptance of energy-efficient renovations, Deutsche Wohnen has developed a model of how climate protection and social compatibility can come together. The "Concept for Socially Compatible Climate Protection in the Building Sector" aims to significantly increase the rate of refurbishment in existing buildings in order to achieve national climate protection targets. At the same time, an economic stimulus package worth billions is being initiated.
 30.06.2020 - 16 players in the German financial sector, with assets of more than €5.5 trillion and over 46 million customer connections in Germany, have signed a voluntary commitment to align their loan and investment portfolios in line with the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement. Through the agreed measurement, publication and target setting to reduce the emissions associated with the loan and investment portfolios, the financial sector intends to make a contribution to climate protection and support the sustainable and future-oriented further development of the economy. This brings the German financial centre one step closer to the goal set by the German government at the beginning of 2019 of making Germany one of the leading locations for sustainable finance.
30.06.2020 - 16 players in the German financial sector, with assets of more than €5.5 trillion and over 46 million customer connections in Germany, have signed a voluntary commitment to align their loan and investment portfolios in line with the goals of the Paris Climate Agreement. Through the agreed measurement, publication and target setting to reduce the emissions associated with the loan and investment portfolios, the financial sector intends to make a contribution to climate protection and support the sustainable and future-oriented further development of the economy. This brings the German financial centre one step closer to the goal set by the German government at the beginning of 2019 of making Germany one of the leading locations for sustainable finance.
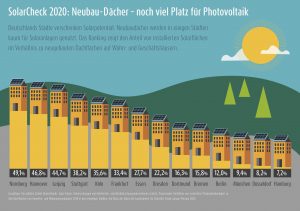 Good news for the PV industry: The solar cap will be abolished and solar expansion will be further promoted. The photovoltaic potential in Germany is enormous - especially when it comes to using roof space on new buildings. The new LichtBlick SolarCheck now shows in detail how well the 14 largest German cities are currently exploiting this potential. Enormous differences are revealed: While Nuremberg (49.1%) and Hanover (46.8%) exploit almost half of their potential, Munich and Düsseldorf do not even reach the 10 percent hurdle. The absolute taillight: the Hanseatic city of Hamburg with only 7.2 percent - one more reason for the solar obligation for new buildings planned by the mayor's office.
Good news for the PV industry: The solar cap will be abolished and solar expansion will be further promoted. The photovoltaic potential in Germany is enormous - especially when it comes to using roof space on new buildings. The new LichtBlick SolarCheck now shows in detail how well the 14 largest German cities are currently exploiting this potential. Enormous differences are revealed: While Nuremberg (49.1%) and Hanover (46.8%) exploit almost half of their potential, Munich and Düsseldorf do not even reach the 10 percent hurdle. The absolute taillight: the Hanseatic city of Hamburg with only 7.2 percent - one more reason for the solar obligation for new buildings planned by the mayor's office.
Am 20. Juni ist kalendarischer Sommeranfang und vielerorts sind schon jetzt Trockenheit und niedrige Wasserstände in den Flüssen an der Tagesordnung, die Gewässer in Deutschland sind nicht gegen die Auswirkungen des Klimawandels gerüstet. Angesichts der verheerenden Zustände vieler Gewässer in Deutschland fordert der BUND einen Paradigmenwechsel im Umgang mit unseren Gewässern: Oberstes Prinzip in Zeiten des Klimawandels muss sein, Wasser in der Landschaft zu halten und Bächen und Flüssen ihre natürliche Dynamik innerhalb ihrer Auen zurückzugeben. Nur knapp acht Prozent der Flüsse und Bäche in Deutschland erreichen den von der europäischen Wasserrahmenrichtlinie geforderten guten ökologischen Zustand. Knapp 40 Prozent der oberirdischen Gewässer sind europaweit durch vielfältige Stressoren wie Klimawandel, Nährstoffeinträge durch die Landwirtschaft oder Begradigungen belastet. "Wir heizen die Erde weiter auf, gleichzeitig entwässern wir die Landschaft. Deshalb ist es keine Überraschung, dass es unseren heimischen Gewässern so schlecht geht", betont Olaf Bandt, Vorsitzender des BUND, mit Blick auf eine aktuelle Auswertung des BUND zu den Auswirkungen des Klimawandels auf Gewässer.
The parliament of Bremen wants to oblige the use of solar energy on all new and existing buildings in Bremen and Bremerhaven. Whenever the roof surface is completely renewed, they are to be equipped with a solar system in the future. This is photovoltaics and, if necessary, also solar thermal energy. The Senate is currently examining the latter.
Lecture "Can we build our way out of the climate crisis?" from 16 April 2020
Among other things, Schellnhuber calls for "prompt measures to achieve the two-degree target, above all by switching from fossil to renewable energy sources and replacing finite building materials with wood and renewable raw materials."
























