Net public electricity generation reached a record share of 59.7 per cent in 2023. The share of the load was 57.1 per cent. This is the result of an analysis presented today by the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE. New records were set for wind and solar power in 2023. In contrast, generation from lignite (-27 per cent) and hard coal (-35 per cent) fell sharply. Photovoltaics stood out in the expansion of generation capacity: at around 14 gigawatts, the expansion was in double digits for the first time and significantly exceeded the German government's statutory climate protection target.
Net public electricity generation reached a record share of 59.7 per cent in 2023. The share of the load was 57.1 per cent. This is the result of an analysis presented today by the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE. New records were set for wind and solar power in 2023. In contrast, generation from lignite (-27 per cent) and hard coal (-35 per cent) fell sharply. Photovoltaics stood out in the expansion of generation capacity: at around 14 gigawatts, the expansion was in double digits for the first time and significantly exceeded the German government's statutory climate protection target.
Kategorie für Blog: New books and studies
More rail transport, reformed motor vehicle tax and less fossil heating needed
 Germany can still achieve its climate targets by 2030. This is shown in a new analysis by the Federal Environment Agency (UBA). This would require, among other things, more rail transport, a reform of the motor vehicle tax and the restriction of fossil heating. In addition, all emissions would have to be priced and charged to the polluter. In the so-called Climate Protection Instruments Scenario 2030 (KIS-2030), the UBA has examined how additional emissions can be saved in the building, mobility, energy and industry sectors. "The model calculation clearly shows that we have a lot of catching up to do in some sectors," says UBA President Dirk Messner. "We now urgently need a constructive dialogue about where emissions can be reduced, otherwise we will miss the legal savings targets. We also need to talk honestly about how to cushion the financial burden on lower-income groups and distribute it more fairly. Currently, low-income households are often asked to pay disproportionately. Understandably, this does not exactly increase acceptance for more climate protection.
Germany can still achieve its climate targets by 2030. This is shown in a new analysis by the Federal Environment Agency (UBA). This would require, among other things, more rail transport, a reform of the motor vehicle tax and the restriction of fossil heating. In addition, all emissions would have to be priced and charged to the polluter. In the so-called Climate Protection Instruments Scenario 2030 (KIS-2030), the UBA has examined how additional emissions can be saved in the building, mobility, energy and industry sectors. "The model calculation clearly shows that we have a lot of catching up to do in some sectors," says UBA President Dirk Messner. "We now urgently need a constructive dialogue about where emissions can be reduced, otherwise we will miss the legal savings targets. We also need to talk honestly about how to cushion the financial burden on lower-income groups and distribute it more fairly. Currently, low-income households are often asked to pay disproportionately. Understandably, this does not exactly increase acceptance for more climate protection.
Environmental crises jeopardise health. At the same time, an ecological change of direction offers many opportunities to create healthier living conditions. This is the core message of the special report that the Environmental Council is presenting to Environment Minister Steffi Lemke and Health Minister Prof Karl Lauterbach in Berlin today. The WHO estimates that 15 % of deaths in Europe are attributable to environmental risks. Health hazards arise, for example, from air pollutants, noise, chemicals and the spread of antibiotic resistance. New pressures, such as climate change and biodiversity loss, are also emerging.
Proven work aid and at the same time standard work for climate protection work in municipalities can be used digitally in future. Difu, ifeu and Climate Alliance developed the guide on behalf of the BMWK.
The bioeconomy can be a central building block for the transformation of our largely coal, oil and gas-based economy. However, renewable raw materials and synthetic carbon compounds are scarce and expensive. They should be used in areas such as the chemical industry - not as energy sources. For the shift from a fossil-based economy to a bioeconomy to succeed, fossil carbon must also become more expensive. The ifeu now presents the results of four trend-setting studies.
The first results of the timber housing study will be presented at the 15th Congress on Efficient Building with Wood in Urban Areas on 19 October 2022 in Cologne. So far, 118 large-volume housing projects with more than 100 units have been identified across Europe by the HFR researchers, 47 of which are located in Germany. Final results will be presented in early December at the 26th International Timber Construction Forum in Innsbruck on 30 November 2022 and will also be published in a brochure by Informationsdienst Holz.
Is German climate policy on the right path? A national CO2 budget for Germany allows for a transparent comparison with international targets. In a paper published today, the Environmental Council updates its calculations for a German CO2 budget, showing that fast emission reductions are crucial - last year, climate targets for transport and buildings were missed again. The paper also answers frequently asked questions about the CO2 budget.
Recommendations from the BMBF project "Urban Heat Transition" were published: ► Consistently tapping alternative heat sources such as wastewater heat ► Convert public buildings to renewable heat and create neighbourhood heating networks ► Ambitious energy refurbishment in neighbourhood conservation areas to keep rents affordable
 Isabella Marboe (ed.) Bauen für die Gemeinschaft in Wien Neue gemeinschaftliche Formen des Zusammenlebens Edition Detail 2021, 144 pages, de/eng, Euro 39,90
The housing projects presented in Vienna arose from the desire to develop living concepts that strengthen the sense of community and contribute to a society based on solidarity - building groups and participatory projects, neighbourhood houses, temporary or permanent social forms of living and working for marginalised groups such as the homeless and people entitled to asylum. Private flats can be downsized if there is more shared space. These housing and living models are alternatives to capitalist investor thinking. The users get involved, also in the project planning. Ulrike Schartner and Alexander Hagner from gaupenraup+/- explain the starting point and strategies of their work in an introductory interview. In two essays, Robert Temel and Isabella Marboe show the development of communal forms of building and living.
Isabella Marboe (ed.) Bauen für die Gemeinschaft in Wien Neue gemeinschaftliche Formen des Zusammenlebens Edition Detail 2021, 144 pages, de/eng, Euro 39,90
The housing projects presented in Vienna arose from the desire to develop living concepts that strengthen the sense of community and contribute to a society based on solidarity - building groups and participatory projects, neighbourhood houses, temporary or permanent social forms of living and working for marginalised groups such as the homeless and people entitled to asylum. Private flats can be downsized if there is more shared space. These housing and living models are alternatives to capitalist investor thinking. The users get involved, also in the project planning. Ulrike Schartner and Alexander Hagner from gaupenraup+/- explain the starting point and strategies of their work in an introductory interview. In two essays, Robert Temel and Isabella Marboe show the development of communal forms of building and living.
 Author of the book review: Roman Schaurhofer, Vienna
The construction volume "Commercial Buildings in Clay and Wood - Added Value through Material" was published in 2020 by Sabine Djahanschah of the Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (German Federal Foundation for the Environment) at Verlag Detail. The publication, which appeared in book form, deals with the use of the building materials wood and clay in the construction of commercially used buildings. To this end, six buildings with commercial use were analysed in terms of their architectural construction and technical quality features and evaluated with the help of measurements, surveys and life cycle assessments.
Author of the book review: Roman Schaurhofer, Vienna
The construction volume "Commercial Buildings in Clay and Wood - Added Value through Material" was published in 2020 by Sabine Djahanschah of the Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt (German Federal Foundation for the Environment) at Verlag Detail. The publication, which appeared in book form, deals with the use of the building materials wood and clay in the construction of commercially used buildings. To this end, six buildings with commercial use were analysed in terms of their architectural construction and technical quality features and evaluated with the help of measurements, surveys and life cycle assessments.
 The new National Progress Report on the Implementation of the New Urban Agenda shows the state of sustainability in urban development in German municipalities. The report was prepared by the German Institute of Urban Affairs on behalf of the Federal Institute for Research on Building, Urban Affairs and Spatial Development (BBSR).
The new National Progress Report on the Implementation of the New Urban Agenda shows the state of sustainability in urban development in German municipalities. The report was prepared by the German Institute of Urban Affairs on behalf of the Federal Institute for Research on Building, Urban Affairs and Spatial Development (BBSR).
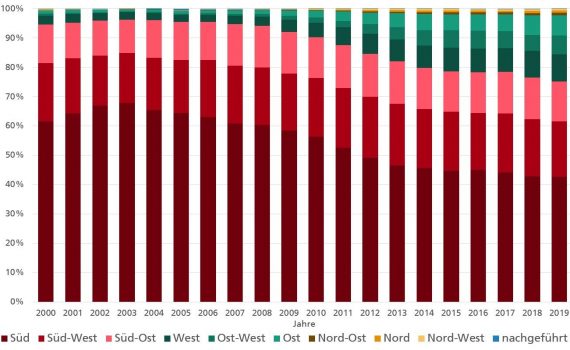
 In a recently written short study, scientists from the Department of Energy System Analysis at the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE prepared an evaluation of the Market Master Data Register (MaStR) and the EEG system master data for photovoltaics (PV). Important findings of the analyses were that with 38 percent of the newly installed capacity, the increase in capacity in Germany is increasingly taking place in the segment of rooftop systems larger than 100 kW, 22 percent of the newly built PV systems are erected in a west, east or east-west direction and 19 percent of these systems have tilt angles smaller than 20 degrees.
In a recently written short study, scientists from the Department of Energy System Analysis at the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE prepared an evaluation of the Market Master Data Register (MaStR) and the EEG system master data for photovoltaics (PV). Important findings of the analyses were that with 38 percent of the newly installed capacity, the increase in capacity in Germany is increasingly taking place in the segment of rooftop systems larger than 100 kW, 22 percent of the newly built PV systems are erected in a west, east or east-west direction and 19 percent of these systems have tilt angles smaller than 20 degrees.
 In a research project of the iaw, the conceptual foundations of urban production and the productive city were prepared with a view to the situation in Bremen and analysed in their impact structure. The study makes proposals for describing and recording urban production that is compatible with the city and embedding it in an urban development policy model of a productive city. On the basis of seven reference cities (Vienna, Zurich, Stuttgart, Hamburg, Frankfurt am Main, Wuppertal, Bochum), corresponding activities were filtered out and their transferability to the city of Bremen was examined. In the city of Bremen, eight locations and neighbourhoods (including the Tabakquartier and Kellogg-Areal) were examined with regard to their potential for implementing a productive city.
In a research project of the iaw, the conceptual foundations of urban production and the productive city were prepared with a view to the situation in Bremen and analysed in their impact structure. The study makes proposals for describing and recording urban production that is compatible with the city and embedding it in an urban development policy model of a productive city. On the basis of seven reference cities (Vienna, Zurich, Stuttgart, Hamburg, Frankfurt am Main, Wuppertal, Bochum), corresponding activities were filtered out and their transferability to the city of Bremen was examined. In the city of Bremen, eight locations and neighbourhoods (including the Tabakquartier and Kellogg-Areal) were examined with regard to their potential for implementing a productive city.
A new study from Denmark takes a look at the costs of sustainable building construction and shows that more sustainable does not automatically mean more expensive. On the contrary. The study by Buus Consult on behalf of the DGNB system partner from Denmark, the Green Building Council Denmark, now provides clarity. In the study, it takes a close look at 37 DGNB-certified buildings.
 In the context of the Green Deal, the EU's tightened targets on the path to climate neutrality envisage a reduction in CO2 emissions of 55% by 2030 and 100% by 2050. Against the background of these tightened parameters, the question arises as to the impact on the energy transition in Germany. Based on its energy system model REMod, Fraunhofer ISE has calculated the consequences of the new EU targets for the expansion of renewable energies in Germany and now presents the results in a short study.
In the context of the Green Deal, the EU's tightened targets on the path to climate neutrality envisage a reduction in CO2 emissions of 55% by 2030 and 100% by 2050. Against the background of these tightened parameters, the question arises as to the impact on the energy transition in Germany. Based on its energy system model REMod, Fraunhofer ISE has calculated the consequences of the new EU targets for the expansion of renewable energies in Germany and now presents the results in a short study.
 The German Sustainable Building Council (DGNB e.V.) has published a new report explaining how buildings can contribute to the United Nations' global sustainability goals. The publication compares the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) with the potential influence of sustainable planning and construction. Architects and planners, as well as building owners and municipalities, are thus provided with orientation as to how they can meaningfully become active in terms of sustainable development. The report also offers a comparison of the SDGs with the criteria of various DGNB certification systems. This shows: Up to 15 of the 17 SDGs are addressed in the context of the DGNB certification of a building project.
The German Sustainable Building Council (DGNB e.V.) has published a new report explaining how buildings can contribute to the United Nations' global sustainability goals. The publication compares the 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) with the potential influence of sustainable planning and construction. Architects and planners, as well as building owners and municipalities, are thus provided with orientation as to how they can meaningfully become active in terms of sustainable development. The report also offers a comparison of the SDGs with the criteria of various DGNB certification systems. This shows: Up to 15 of the 17 SDGs are addressed in the context of the DGNB certification of a building project.
 The ecological model settlement on a former barracks site in Munich sets new standards in timber construction. Various timber construction methods and building types up to seven storeys are being tested side by side in eight building projects with the aim of a final scientific evaluation. Timber frame, timber frame and timber hybrid construction methods are being used.
The ecological model settlement on a former barracks site in Munich sets new standards in timber construction. Various timber construction methods and building types up to seven storeys are being tested side by side in eight building projects with the aim of a final scientific evaluation. Timber frame, timber frame and timber hybrid construction methods are being used.
 Since April 2020, the Öko-Institut has been conducting research into how urban neighbourhoods can be sustainably transformed, using two neighbourhoods in the swarming city of Darmstadt as examples, in the project Transformative Strategies for Integrated Neighbourhood Development (TRASIQ 2). The Federal Ministry of Education and Research is funding the project, which is led by the Öko-Institut and involves the City of Darmstadt, the Institute for Regional and Urban Development Research (ILS) and the "Team Ewen" agency.
Since April 2020, the Öko-Institut has been conducting research into how urban neighbourhoods can be sustainably transformed, using two neighbourhoods in the swarming city of Darmstadt as examples, in the project Transformative Strategies for Integrated Neighbourhood Development (TRASIQ 2). The Federal Ministry of Education and Research is funding the project, which is led by the Öko-Institut and involves the City of Darmstadt, the Institute for Regional and Urban Development Research (ILS) and the "Team Ewen" agency.
Mobility, heat and living space
The project focuses on the research topics of mobility, heat supply and efficient use of living space. Heat supply is an important key to climate-friendly living. How and where, for example, can district heating be expanded in existing properties? How can we increase the share of renewable energies in the heat supply? The size of the living space also contributes to how environmentally friendly a person lives. What needs to be done to ensure that people have the living space they need in their particular phase of life through intelligent apartment swaps? How can neighbourhoods be redesigned so that residents can organise their mobility ecologically? With the gradual dismantling of ten particularly climate-damaging subsidies in the energy, transport and agricultural sectors, Germany could generate up to 46 billion euros in revenue annually. This is the result of a new study by the "Forum Ökologisch-Soziale Marktwirtschaft" commissioned by Greenpeace.
With the gradual dismantling of ten particularly climate-damaging subsidies in the energy, transport and agricultural sectors, Germany could generate up to 46 billion euros in revenue annually. This is the result of a new study by the "Forum Ökologisch-Soziale Marktwirtschaft" commissioned by Greenpeace.
 Dr. Kirsten David, a researcher at HafenCity University (HCU) Hamburg, has developed an innovative method for determining rent increases after energy efficiency measures: By means of functional cost splitting, rent increases become appropriate and comprehensible. The planning of the energetic measures is also ecologically optimized. For her dissertation entitled "Functional Cost Splitting for the Determination of Rent Increases after Energy Efficiency Measures", the scientist today receives the "BUND Research Award 2020". With the research award, the Bund für Umwelt- und Naturschutz (BUND) honors scientific work on sustainable development.
Dr. Kirsten David, a researcher at HafenCity University (HCU) Hamburg, has developed an innovative method for determining rent increases after energy efficiency measures: By means of functional cost splitting, rent increases become appropriate and comprehensible. The planning of the energetic measures is also ecologically optimized. For her dissertation entitled "Functional Cost Splitting for the Determination of Rent Increases after Energy Efficiency Measures", the scientist today receives the "BUND Research Award 2020". With the research award, the Bund für Umwelt- und Naturschutz (BUND) honors scientific work on sustainable development.
 Glaciers are melting, sea levels are rising, heat waves and heavy rainfall are increasing: The consequences of climate change are visible and tangible worldwide, and the window of opportunity to act is shrinking. In order to significantly limit the global effects of climate change, the emission of greenhouse gases on earth must be drastically reduced. The agreement reached by the international community in Paris in 2015 sets the goal of limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, but preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius. Now, the Wuppertal Institute presented a study with possible cornerstones that can help to achieve the 1.5 degree target by 2035. The study shows that a climate-neutral energy system by 2035 is very ambitious, but in principle feasible, provided that all possible strategies from today's perspective are bundled. This requires, above all, bringing forward and intensifying measures that are described in many studies as necessary to achieve greenhouse gas neutrality by 2050.
Glaciers are melting, sea levels are rising, heat waves and heavy rainfall are increasing: The consequences of climate change are visible and tangible worldwide, and the window of opportunity to act is shrinking. In order to significantly limit the global effects of climate change, the emission of greenhouse gases on earth must be drastically reduced. The agreement reached by the international community in Paris in 2015 sets the goal of limiting global warming to well below 2 degrees Celsius, but preferably to 1.5 degrees Celsius. Now, the Wuppertal Institute presented a study with possible cornerstones that can help to achieve the 1.5 degree target by 2035. The study shows that a climate-neutral energy system by 2035 is very ambitious, but in principle feasible, provided that all possible strategies from today's perspective are bundled. This requires, above all, bringing forward and intensifying measures that are described in many studies as necessary to achieve greenhouse gas neutrality by 2050.
 The Institute for Urban Planning and Social Research WEEBER+PARTNER (Stuttgart) examined 16 case studies and interviewed responsible persons in municipal, cooperative and private housing companies. The projects are characterized by a wide range of planning and construction approaches. According to the study, social diversity requires structural diversity: Rental, social and owner-occupied apartments of different sizes and with diverse layouts were created in the new housing quarters. They are socially mixed - even within buildings - with the respective proportions in the neighbourhood being derived from local requirements. The new quarters also offer space for communal forms of living, for example for older people and those in need of care. And they are characterised by an attractively designed and green residential environment. Concept awards promote the planning and implementation of such projects: Through them, plots of land are not allocated according to the highest price, but for the best concept.
The Institute for Urban Planning and Social Research WEEBER+PARTNER (Stuttgart) examined 16 case studies and interviewed responsible persons in municipal, cooperative and private housing companies. The projects are characterized by a wide range of planning and construction approaches. According to the study, social diversity requires structural diversity: Rental, social and owner-occupied apartments of different sizes and with diverse layouts were created in the new housing quarters. They are socially mixed - even within buildings - with the respective proportions in the neighbourhood being derived from local requirements. The new quarters also offer space for communal forms of living, for example for older people and those in need of care. And they are characterised by an attractively designed and green residential environment. Concept awards promote the planning and implementation of such projects: Through them, plots of land are not allocated according to the highest price, but for the best concept.
 Conceptual procedures are increasingly establishing themselves as a further instrument of municipal land policy for locations with development potential. Here, the property is not allocated according to the highest price, but according to the concept that promises the most sustainable approaches to the further development of the neighbourhood. In this way, the procedures offer municipalities approaches to solving two current and urgent problems: the need for high-quality urban development and affordable housing.
Conceptual procedures are increasingly establishing themselves as a further instrument of municipal land policy for locations with development potential. Here, the property is not allocated according to the highest price, but according to the concept that promises the most sustainable approaches to the further development of the neighbourhood. In this way, the procedures offer municipalities approaches to solving two current and urgent problems: the need for high-quality urban development and affordable housing.
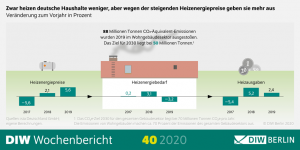 Annual DIW Heat Monitor based on data from energy service provider ista Deutschland GmbH: Heating energy demand in residential buildings declines again for the first time since 2015 - Rising prices, however, cause heating expenditure to increase by 2.4 percent - CO2emissions have fallen by 21 percent overall since 2010, but by only 2.6 percent when adjusted for temperature - Energy-efficient renovation in residential buildings almost stagnant
Annual DIW Heat Monitor based on data from energy service provider ista Deutschland GmbH: Heating energy demand in residential buildings declines again for the first time since 2015 - Rising prices, however, cause heating expenditure to increase by 2.4 percent - CO2emissions have fallen by 21 percent overall since 2010, but by only 2.6 percent when adjusted for temperature - Energy-efficient renovation in residential buildings almost stagnant
 A study funded by the Federal Ministry of Agriculture determined the potential of hardwood as a substitute for coniferous wood. The results of the study are now available in a brochure published by the Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e. V. (FNR). There is considerable potential for hardwood to be used in industrial timber, but it cannot yet be a substitute for softwood in construction
A study funded by the Federal Ministry of Agriculture determined the potential of hardwood as a substitute for coniferous wood. The results of the study are now available in a brochure published by the Fachagentur Nachwachsende Rohstoffe e. V. (FNR). There is considerable potential for hardwood to be used in industrial timber, but it cannot yet be a substitute for softwood in construction
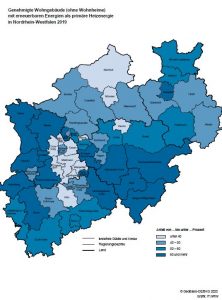
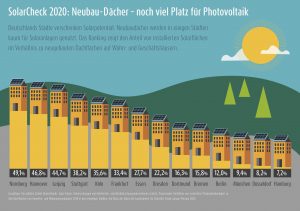 Good news for the PV industry: The solar cap will be abolished and solar expansion will be further promoted. The photovoltaic potential in Germany is enormous - especially when it comes to using roof space on new buildings. The new LichtBlick SolarCheck now shows in detail how well the 14 largest German cities are currently exploiting this potential. Enormous differences are revealed: While Nuremberg (49.1%) and Hanover (46.8%) exploit almost half of their potential, Munich and Düsseldorf do not even reach the 10 percent hurdle. The absolute taillight: the Hanseatic city of Hamburg with only 7.2 percent - one more reason for the solar obligation for new buildings planned by the mayor's office.
Good news for the PV industry: The solar cap will be abolished and solar expansion will be further promoted. The photovoltaic potential in Germany is enormous - especially when it comes to using roof space on new buildings. The new LichtBlick SolarCheck now shows in detail how well the 14 largest German cities are currently exploiting this potential. Enormous differences are revealed: While Nuremberg (49.1%) and Hanover (46.8%) exploit almost half of their potential, Munich and Düsseldorf do not even reach the 10 percent hurdle. The absolute taillight: the Hanseatic city of Hamburg with only 7.2 percent - one more reason for the solar obligation for new buildings planned by the mayor's office.
Am 20. Juni ist kalendarischer Sommeranfang und vielerorts sind schon jetzt Trockenheit und niedrige Wasserstände in den Flüssen an der Tagesordnung, die Gewässer in Deutschland sind nicht gegen die Auswirkungen des Klimawandels gerüstet. Angesichts der verheerenden Zustände vieler Gewässer in Deutschland fordert der BUND einen Paradigmenwechsel im Umgang mit unseren Gewässern: Oberstes Prinzip in Zeiten des Klimawandels muss sein, Wasser in der Landschaft zu halten und Bächen und Flüssen ihre natürliche Dynamik innerhalb ihrer Auen zurückzugeben. Nur knapp acht Prozent der Flüsse und Bäche in Deutschland erreichen den von der europäischen Wasserrahmenrichtlinie geforderten guten ökologischen Zustand. Knapp 40 Prozent der oberirdischen Gewässer sind europaweit durch vielfältige Stressoren wie Klimawandel, Nährstoffeinträge durch die Landwirtschaft oder Begradigungen belastet. "Wir heizen die Erde weiter auf, gleichzeitig entwässern wir die Landschaft. Deshalb ist es keine Überraschung, dass es unseren heimischen Gewässern so schlecht geht", betont Olaf Bandt, Vorsitzender des BUND, mit Blick auf eine aktuelle Auswertung des BUND zu den Auswirkungen des Klimawandels auf Gewässer.
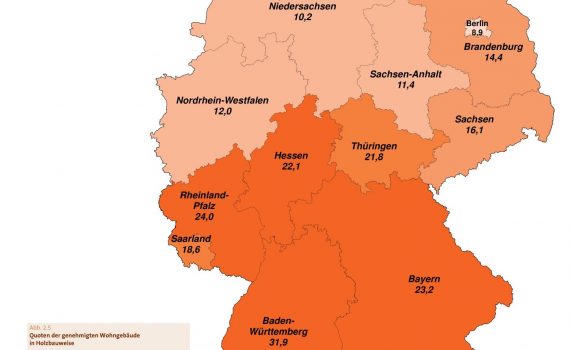
 The discussion about climate change and the growing demand for living space have increasingly brought timber construction into the focus of planners, architects and developers over the past year. After all, sustainable timber construction can make a significant contribution to climate protection and the creation of living space. The increased interest in timber construction is also reflected in the industry figures: the turnover of companies grew by 7 percent in 2019 compared to the previous year, the number of employees increased from around 68,000 to around 70,000 and the timber construction rate continued to grow in both residential (new construction) and non-residential (new construction) construction.
The discussion about climate change and the growing demand for living space have increasingly brought timber construction into the focus of planners, architects and developers over the past year. After all, sustainable timber construction can make a significant contribution to climate protection and the creation of living space. The increased interest in timber construction is also reflected in the industry figures: the turnover of companies grew by 7 percent in 2019 compared to the previous year, the number of employees increased from around 68,000 to around 70,000 and the timber construction rate continued to grow in both residential (new construction) and non-residential (new construction) construction.
 Berlin/Cologne. Climate protection and adaptation to the consequences of climate change will become increasingly important for cities. This is one of the findings of the survey of (Lord) Mayors of large German cities* conducted by the German Institute of Urban Affairs in January and February 2020. Almost two-thirds of the respondents named climate protection as an important municipal issue for the future. This means that the number of mayors who attribute an increase in importance to this field of municipal policy action has more than tripled compared to the previous year. Future surveys will show how strongly this result was influenced by the protests of the 'Fridays for Future' movement.
Berlin/Cologne. Climate protection and adaptation to the consequences of climate change will become increasingly important for cities. This is one of the findings of the survey of (Lord) Mayors of large German cities* conducted by the German Institute of Urban Affairs in January and February 2020. Almost two-thirds of the respondents named climate protection as an important municipal issue for the future. This means that the number of mayors who attribute an increase in importance to this field of municipal policy action has more than tripled compared to the previous year. Future surveys will show how strongly this result was influenced by the protests of the 'Fridays for Future' movement.
 Eine Studie des Forums Ökologisch-Soziale Marktwirtschaft im Auftrag von Greenpeace (März 2020).
Durch die Corona-Krise wird der Staat Soforthilfen und weitreichende Konjunkturmaßnahmen historischen Ausmaßes umsetzen. Während Gesundheit und die kurzfristige Unterstützung von Arbeitnehmer*innen und Unternehmen in den Fokus rücken, dürfen die Fehler vergangener Wirtschaftskrisen nicht wiederholt werden. Die geplanten Hilfen für einen wirtschaftlichen Neustart können die Weichen stellen für die notwendige Transformation. Anhand einiger Beispiele wird illustriert, wie kurzfristige wirtschaftliche Unterstützung mit langfristigen gesellschaftlichen Prioritäten in Einklang gebracht werden können.
Eine Studie des Forums Ökologisch-Soziale Marktwirtschaft im Auftrag von Greenpeace (März 2020).
Durch die Corona-Krise wird der Staat Soforthilfen und weitreichende Konjunkturmaßnahmen historischen Ausmaßes umsetzen. Während Gesundheit und die kurzfristige Unterstützung von Arbeitnehmer*innen und Unternehmen in den Fokus rücken, dürfen die Fehler vergangener Wirtschaftskrisen nicht wiederholt werden. Die geplanten Hilfen für einen wirtschaftlichen Neustart können die Weichen stellen für die notwendige Transformation. Anhand einiger Beispiele wird illustriert, wie kurzfristige wirtschaftliche Unterstützung mit langfristigen gesellschaftlichen Prioritäten in Einklang gebracht werden können.
 In research, neighbourhoods have been recognised as an important level of action for climate protection. For this reason, the BMBF, BMU and the Federal Ministry of Building and Transport have funded several research projects on sustainable neighbourhoods, which are now being worked on. The consensus of the research projects presented and the funding bodies is that it is important to research neighbourhood concepts for a climate-friendly heat and electricity supply as well as an environmentally friendly mobility offer in an economical way" and "to link the individual elements in the sense of a functioning sector coupling in a meaningful way."
The focus articles in the "Ecological Economy 3/2019" issue highlight the potential of the neighbourhood approach for the implementation of climate protection measures, but also present best practice examples and discuss feasibility in practice.
In research, neighbourhoods have been recognised as an important level of action for climate protection. For this reason, the BMBF, BMU and the Federal Ministry of Building and Transport have funded several research projects on sustainable neighbourhoods, which are now being worked on. The consensus of the research projects presented and the funding bodies is that it is important to research neighbourhood concepts for a climate-friendly heat and electricity supply as well as an environmentally friendly mobility offer in an economical way" and "to link the individual elements in the sense of a functioning sector coupling in a meaningful way."
The focus articles in the "Ecological Economy 3/2019" issue highlight the potential of the neighbourhood approach for the implementation of climate protection measures, but also present best practice examples and discuss feasibility in practice.
 From the meeting of the Senate on 10 March 2020:
The Senate today adopted a comprehensive catalogue of measures to accelerate the expansion of solar energy in Berlin, following a proposal by the Senator for Economics, Energy and Public Enterprises, Ramona Pop.
Senator Pop: "The potential study for the Solarcity Masterplan has shown that we can harvest 25 per cent of the electricity generated with solar energy from Berlin's rooftops. We must therefore accelerate the expansion of solar energy in the city. It is necessary for the federal government to finally improve the legal framework for solar energy in cities. Nevertheless, we want to actively utilise the available scope at state level. With the Solarcity Masterplan, we will expand information and advice, provide incentives and also examine regulatory instruments. The implementation of the Solarcity Masterplan is a joint task for the Senate, but also for all Berlin stakeholders from business and society."
From the meeting of the Senate on 10 March 2020:
The Senate today adopted a comprehensive catalogue of measures to accelerate the expansion of solar energy in Berlin, following a proposal by the Senator for Economics, Energy and Public Enterprises, Ramona Pop.
Senator Pop: "The potential study for the Solarcity Masterplan has shown that we can harvest 25 per cent of the electricity generated with solar energy from Berlin's rooftops. We must therefore accelerate the expansion of solar energy in the city. It is necessary for the federal government to finally improve the legal framework for solar energy in cities. Nevertheless, we want to actively utilise the available scope at state level. With the Solarcity Masterplan, we will expand information and advice, provide incentives and also examine regulatory instruments. The implementation of the Solarcity Masterplan is a joint task for the Senate, but also for all Berlin stakeholders from business and society."
 Konturen einer solidarischen Stadtpolitik
Anton Brokow-Loga (Hrsg.),
Frank Eckardt (Hrsg.)
Städte ohne Wachstum – eine bislang kaum vorstellbare Vision. Doch Klimawandel,
Ressourcenverschwendung, wachsende soziale Ungleichheiten und viele andere
Zukunftsgefahren stellen das bisherige Allheilmittel Wachstum grundsätzlich infrage. Wie wollen
wir heute und morgen zusammenleben? Wie gestalten wir ein gutes Leben für alle in der Stadt?
Konturen einer solidarischen Stadtpolitik
Anton Brokow-Loga (Hrsg.),
Frank Eckardt (Hrsg.)
Städte ohne Wachstum – eine bislang kaum vorstellbare Vision. Doch Klimawandel,
Ressourcenverschwendung, wachsende soziale Ungleichheiten und viele andere
Zukunftsgefahren stellen das bisherige Allheilmittel Wachstum grundsätzlich infrage. Wie wollen
wir heute und morgen zusammenleben? Wie gestalten wir ein gutes Leben für alle in der Stadt?
- Over EUR 28 billion for "climate protection measures": KfW is one of the most important supporters of the Paris climate goals
- Promotional bank is a global pioneer with its standardised SDG mapping
- Strong international interest in KfW SDG mapping
 KfW is today publishing the results of the SDG mapping of new commitments throughout the Group in 2019. In order to clarify the individual contribution made by KfW's new commitments to achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals, KfW has developed a standardised procedure: 1,500 indicators are used each year to determine to which SDGs KfW's new commitments can be assigned. This makes the contribution transparent at both group and business sector level.
KfW is today publishing the results of the SDG mapping of new commitments throughout the Group in 2019. In order to clarify the individual contribution made by KfW's new commitments to achieving the UN Sustainable Development Goals, KfW has developed a standardised procedure: 1,500 indicators are used each year to determine to which SDGs KfW's new commitments can be assigned. This makes the contribution transparent at both group and business sector level.