Charakteristik: Multi-storey housing
 40625 Düsseldorf-Gerresheim: the wmk assembly3 is located on the "Am Quellenbusch" site in the Düsseldorf district of Gerresheim. In the entire construction area, 800 residential units will be built. The completion of the 30 wmk3 apartments was in 2017.
40625 Düsseldorf-Gerresheim: the wmk assembly3 is located on the "Am Quellenbusch" site in the Düsseldorf district of Gerresheim. In the entire construction area, 800 residential units will be built. The completion of the 30 wmk3 apartments was in 2017.
 48143 Münster: Car-free NRW model housing estate "Gartenhofsiedlung Weißenburg", Europe-wide competition, car-reduced mobility concept with 0.2 car parking spaces per flat, 189 flats on 3.8 hectares of land. Completion: 2003 Completion of 2nd construction phase (4 buildings with 51 flats): 2019
48143 Münster: Car-free NRW model housing estate "Gartenhofsiedlung Weißenburg", Europe-wide competition, car-reduced mobility concept with 0.2 car parking spaces per flat, 189 flats on 3.8 hectares of land. Completion: 2003 Completion of 2nd construction phase (4 buildings with 51 flats): 2019
 50733 Cologne-Nippes: "Autofreie Siedlung". 460 Wohnungen für ca. 1.500 Bewohner. Der Stellplatzschlüssel liegt bei 0,2 Pkw je Wohneinheit. Für die Haushalte der Siedlung und für ca. 40 Besucher wurde am Siedlungsrand ein Parkhaus mit 120 Stellplätzen gebaut. Normalerweise wären an dem Standort ca. 400 bis 500 Stellplätze erforderlich gewesen. Fertigstellung: 2013
50733 Cologne-Nippes: "Autofreie Siedlung". 460 Wohnungen für ca. 1.500 Bewohner. Der Stellplatzschlüssel liegt bei 0,2 Pkw je Wohneinheit. Für die Haushalte der Siedlung und für ca. 40 Besucher wurde am Siedlungsrand ein Parkhaus mit 120 Stellplätzen gebaut. Normalerweise wären an dem Standort ca. 400 bis 500 Stellplätze erforderlich gewesen. Fertigstellung: 2013
52072 Aachen-Laurensberg: "Solarsiedlung Teichstraße", 43 residential buildings in 27 terraced houses and 16 semi-detached houses, as well as two office buildings in passive house standard, on 2.5 hectares of land; partly wood pellet heating, 60 % coverage via solar thermal collectors, PV system or geothermal system. Completion: 2003

![]() D - 53115 Bonn: in Bonn's Südstadt, surrounded by residential buildings
D - 53115 Bonn: in Bonn's Südstadt, surrounded by residential buildings
 60327 Frankfurt: Energy-plus building, BMUB-supported. 74 residential units and 2 commercial units, gross floor area: 11,700 m². The building itself generates the energy required by the residents for heating, ventilation, water heating, household, elevator and general electricity. The energy supply including electricity is included in the flat rate rent. Surpluses can be used by the residents for e-mobility. Completion: 2015
60327 Frankfurt: Energy-plus building, BMUB-supported. 74 residential units and 2 commercial units, gross floor area: 11,700 m². The building itself generates the energy required by the residents for heating, ventilation, water heating, household, elevator and general electricity. The energy supply including electricity is included in the flat rate rent. Surpluses can be used by the residents for e-mobility. Completion: 2015
 64289 Darmstadt: Forest spiral, design by Friedensreich Hundertwasser. Model project for the use of recycled concrete.
"Green roofs are the roof coverings of the future. [...] It's hard to imagine that there was once a time when roofs were dead - without life and without vegetation."
Friedensreich Hundertwasser in: Stifter, Roland (1988): Roof gardens: green islands in the city. Stuttgart
64289 Darmstadt: Forest spiral, design by Friedensreich Hundertwasser. Model project for the use of recycled concrete.
"Green roofs are the roof coverings of the future. [...] It's hard to imagine that there was once a time when roofs were dead - without life and without vegetation."
Friedensreich Hundertwasser in: Stifter, Roland (1988): Roof gardens: green islands in the city. Stuttgart
 69115 Heidelberg: Bahnstadt is the largest passive house development in the world and one of the largest new development areas in Germany with 116 ha. Electricity and heat are supplied entirely from renewable energies. 6,500 to 6,800 people will live in Bahnstadt in the future, and 5,000 to 6,000 people will work there. At the end of 2018, more than 4,000 people will live in Bahnstadt. Around 2,450 apartments have already been built - a total of around 3,700 apartments will be built.
69115 Heidelberg: Bahnstadt is the largest passive house development in the world and one of the largest new development areas in Germany with 116 ha. Electricity and heat are supplied entirely from renewable energies. 6,500 to 6,800 people will live in Bahnstadt in the future, and 5,000 to 6,000 people will work there. At the end of 2018, more than 4,000 people will live in Bahnstadt. Around 2,450 apartments have already been built - a total of around 3,700 apartments will be built.

![]() D - 69124 Heidelberg: Under the motto Knowledge creates the city the IBA Heidelberg will take place from 2012 to 2022. One of the key projects of the IBA and its largest urban development project of international significance is the Patrick Henry Village (PHV) where once 8,000 Americans lived. An urban development vision is currently being developed for the conversion project, which covers an area of 92.7 ha, under the leadership of urban planner Kees Christiaanse (KCAP) from Zurich. The preliminary city-wide plans envisage apartments for around 10,000 residents (approx. 4,200 residential units), as well as buildings with space for approx. 5,000 workplaces. Completion: ~2030
D - 69124 Heidelberg: Under the motto Knowledge creates the city the IBA Heidelberg will take place from 2012 to 2022. One of the key projects of the IBA and its largest urban development project of international significance is the Patrick Henry Village (PHV) where once 8,000 Americans lived. An urban development vision is currently being developed for the conversion project, which covers an area of 92.7 ha, under the leadership of urban planner Kees Christiaanse (KCAP) from Zurich. The preliminary city-wide plans envisage apartments for around 10,000 residents (approx. 4,200 residential units), as well as buildings with space for approx. 5,000 workplaces. Completion: ~2030
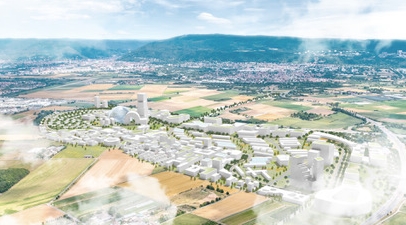
![]() D - 70191 Stuttgart: the city of Stuttgart assumes 7,500 apartments (for 11,000 inhabitants) and 4,000 jobs (as of 2015) on 85 ha. Start: 2026 at the earliest; completion: ~2032
D - 70191 Stuttgart: the city of Stuttgart assumes 7,500 apartments (for 11,000 inhabitants) and 4,000 jobs (as of 2015) on 85 ha. Start: 2026 at the earliest; completion: ~2032
 72072 Tübingen: District development in the French Quarter for 2,500 residents. Around 150 businesses with around 700 jobs have been established. Leisure, shopping and service facilities are planned in the quarter itself or are partly available in the immediate vicinity of the quarter. This is a conversion area with former barracks of the French Army; conversion of the massive barracks buildings, which are worth preserving, to multi-storey housing or redensification on vacant, cleared areas. Completion: 2012
72072 Tübingen: District development in the French Quarter for 2,500 residents. Around 150 businesses with around 700 jobs have been established. Leisure, shopping and service facilities are planned in the quarter itself or are partly available in the immediate vicinity of the quarter. This is a conversion area with former barracks of the French Army; conversion of the massive barracks buildings, which are worth preserving, to multi-storey housing or redensification on vacant, cleared areas. Completion: 2012
 72072 Tübingen-French Quarter: Residential and commercial space: 3,186 m². 34 residential units in two to three-storey maisonettes and 6 commercial units. Joachim Eble architecture. Arcade access to the upper apartments. Apartment partition ceilings in board-stack concrete composite construction; toxically harmless building materials. Water play area in the residential courtyard. Total construction costs (gross): 4,650,000 euros, land costs: 550,000 euros. No basement. Completion date: 2000
72072 Tübingen-French Quarter: Residential and commercial space: 3,186 m². 34 residential units in two to three-storey maisonettes and 6 commercial units. Joachim Eble architecture. Arcade access to the upper apartments. Apartment partition ceilings in board-stack concrete composite construction; toxically harmless building materials. Water play area in the residential courtyard. Total construction costs (gross): 4,650,000 euros, land costs: 550,000 euros. No basement. Completion date: 2000
 72074 Tübingen: with 111 apartments, it is the first large ecological settlement in Germany, GFZ 0.9, open space design according to H. Kügelhaus, building biology, wooden ceilings, natural food shop, naturopathy practice, social housing, planning team: Eble, Sambeth, Oed, Häfele, the first large ecological settlement in Europe. Since 2018, the pioneer settlement is a listed building. Completion: 1985
72074 Tübingen: with 111 apartments, it is the first large ecological settlement in Germany, GFZ 0.9, open space design according to H. Kügelhaus, building biology, wooden ceilings, natural food shop, naturopathy practice, social housing, planning team: Eble, Sambeth, Oed, Häfele, the first large ecological settlement in Europe. Since 2018, the pioneer settlement is a listed building. Completion: 1985
 73760 Ostfildern: Former barracks site. The settlement is designed for 8,000 inhabitants and 2,000 jobs, on 140 hectares. The connecting link and landmark is the "landscape staircase", which is a good kilometre long and 30 metres wide and slopes gently down to the south. The development of energy-efficient buildings and the use of regenerative energies was financially supported with funds from the EU research project POLYCITY (funding period 2005-2010). The complete investment volume of the project with a floor area of 480,700 m² amounts to 1.5 billion euros. German Urban Development Award 2006.
73760 Ostfildern: Former barracks site. The settlement is designed for 8,000 inhabitants and 2,000 jobs, on 140 hectares. The connecting link and landmark is the "landscape staircase", which is a good kilometre long and 30 metres wide and slopes gently down to the south. The development of energy-efficient buildings and the use of regenerative energies was financially supported with funds from the EU research project POLYCITY (funding period 2005-2010). The complete investment volume of the project with a floor area of 480,700 m² amounts to 1.5 billion euros. German Urban Development Award 2006.
74076 Heilbronn: 22 houses are to be built and occupied in the first construction phase by 2019. The development is intended to form a compact, urban edge to the Federal Horticultural Show Heilbronn 2019. 19 renowned offices have designed the architecture for this. The usage concepts are diverse, and technical innovations are to be showcased. A four- to six-storey development is planned for the approximately 30-hectare site. Around 3,500 residents are expected to live here one day. The site is certified as a "DGNB Platinum" for urban neighbourhoods (2016 version).

![]() D - 76131 Karlsruhe-Oststadt: Since 2013, the "Quartier Zukunft" real-world laboratory has been under construction in Karlsruhe, where the urban life of the future is being tested and developed. The city of the future has largely been built in Europe. This means that the major task of sustainable urban development lies in the transformation of the existing.
D - 76131 Karlsruhe-Oststadt: Since 2013, the "Quartier Zukunft" real-world laboratory has been under construction in Karlsruhe, where the urban life of the future is being tested and developed. The city of the future has largely been built in Europe. This means that the major task of sustainable urban development lies in the transformation of the existing.
 76187 Karlsruhe-Nordweststadt: the design was planned for an undeveloped plot of land as a student research project at the University of Karlsruhe in cooperation with the association ASKA e.V., but was not realized. Concept: 140 units, photovoltaic and biomass CHP, business and office facilities, community facilities, gastronomy, car sharing tower, reed sewage treatment plant, board stack wood construction, hemp, flax or cellulose insulation, social settlement concept, integrated living. Completion: not realized
76187 Karlsruhe-Nordweststadt: the design was planned for an undeveloped plot of land as a student research project at the University of Karlsruhe in cooperation with the association ASKA e.V., but was not realized. Concept: 140 units, photovoltaic and biomass CHP, business and office facilities, community facilities, gastronomy, car sharing tower, reed sewage treatment plant, board stack wood construction, hemp, flax or cellulose insulation, social settlement concept, integrated living. Completion: not realized
79110 Freiburg: Architect: Rolf Disch, model project with transparent thermal insulation, renovation of old buildings
 79100 Freiburg-Vauban: extended citizen participation through the Forum Vauban, car-free living, public transport, car sharing, mixed use, solar garage, local heating with CHP units, nature-oriented open space design, building biology and ecological materials. 40% of households live without their own car. The number of parking spaces for the entire quarter is 0.42 PkW/WE. Large-scale completion: 2012
79100 Freiburg-Vauban: extended citizen participation through the Forum Vauban, car-free living, public transport, car sharing, mixed use, solar garage, local heating with CHP units, nature-oriented open space design, building biology and ecological materials. 40% of households live without their own car. The number of parking spaces for the entire quarter is 0.42 PkW/WE. Large-scale completion: 2012
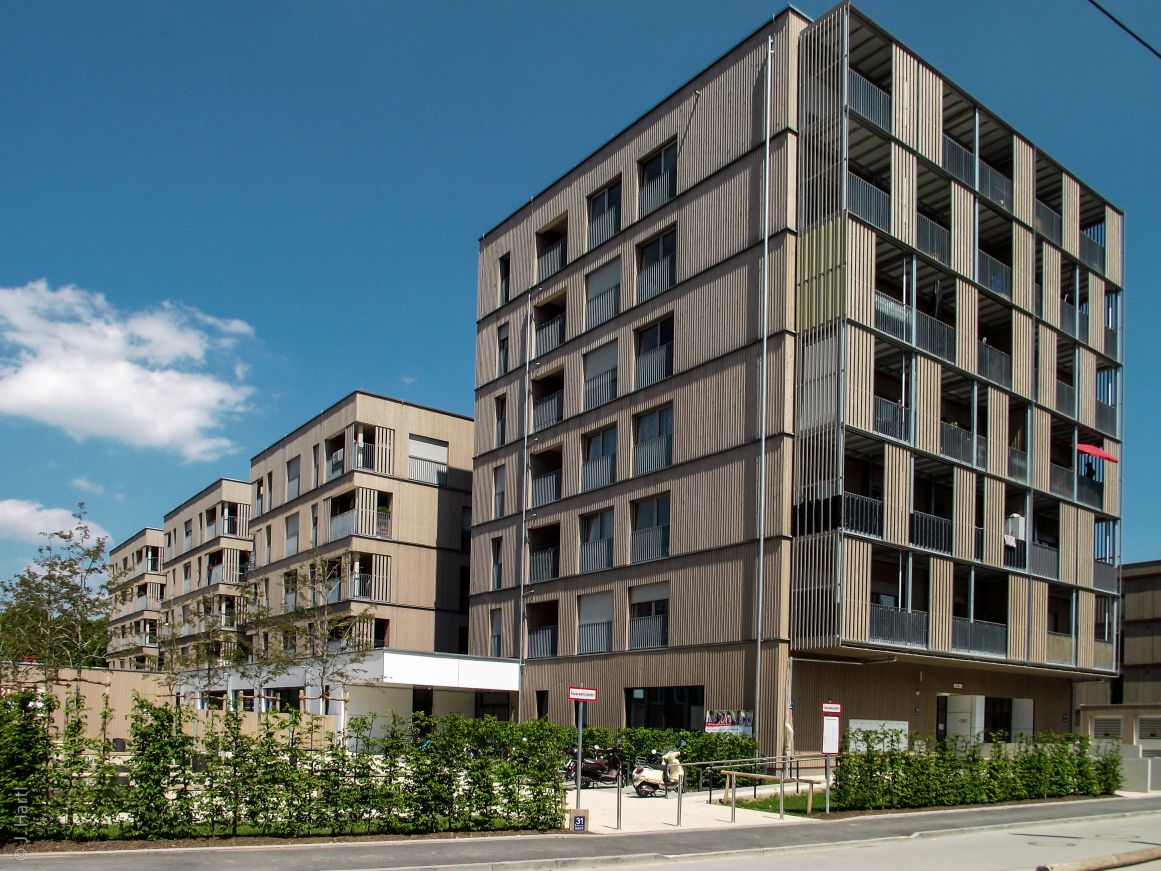 81927 Munich: Germany's largest contiguous timber housing estate with 566 flats in timber or timber hybrid construction has been built in the Oberföhring district. Different building types up to 7-storey houses were built in timber construction. The approximately 30-hectare site of the former Prinz Eugen barracks is located in the Bogenhausen neighbourhood (district 13). The flats were realised by building associations, cooperatives, municipal and independent developers, which means that a wide range of housing can be offered for a wide variety of housing needs: for rent and ownership, in different building types, for all household sizes and income groups and alternative forms of housing. Completion: 2020
81927 Munich: Germany's largest contiguous timber housing estate with 566 flats in timber or timber hybrid construction has been built in the Oberföhring district. Different building types up to 7-storey houses were built in timber construction. The approximately 30-hectare site of the former Prinz Eugen barracks is located in the Bogenhausen neighbourhood (district 13). The flats were realised by building associations, cooperatives, municipal and independent developers, which means that a wide range of housing can be offered for a wide variety of housing needs: for rent and ownership, in different building types, for all household sizes and income groups and alternative forms of housing. Completion: 2020
81829 Munich, Messestadt Riem: 28 apartments, including 6 maisonettes, in 2 houses, low-energy construction. Completion 2001
82223 Eichenau: 96 flats, "Wohnmodelle Bayern", low-energy standard, shared heating centre, roof drainage via a drainage system. Completion: 2003
 90443 Nuremberg: Planning: Joachim Eble Architecture. Property developer: Karlsruher Lebensversicherung AG. Exceptional colour design. "Urban oasis" in an intensively urbanised and sealed city district. Natural air conditioning system with water concept (Ramboll Studio Dreiseitl). Offices and commercial space on the lower floors. One-storey residential building and maisonette apartments on the ground floor with a total of 61 flats. Partly in board stack construction, high building biology standard. Completion: 1997
90443 Nuremberg: Planning: Joachim Eble Architecture. Property developer: Karlsruher Lebensversicherung AG. Exceptional colour design. "Urban oasis" in an intensively urbanised and sealed city district. Natural air conditioning system with water concept (Ramboll Studio Dreiseitl). Offices and commercial space on the lower floors. One-storey residential building and maisonette apartments on the ground floor with a total of 61 flats. Partly in board stack construction, high building biology standard. Completion: 1997
 30539 Hanover-Kronsberg: Reducing energy consumption through low-energy construction, saving electricity and using CHP units. A passive house estate (see "Lummerland estate") and a solar estate with solar local heating and seasonal storage were realised as sub-projects. Intensive green space design. Rainwater is channelled into the trough-trench system. Completion: 2000
30539 Hanover-Kronsberg: Reducing energy consumption through low-energy construction, saving electricity and using CHP units. A passive house estate (see "Lummerland estate") and a solar estate with solar local heating and seasonal storage were realised as sub-projects. Intensive green space design. Rainwater is channelled into the trough-trench system. Completion: 2000